gas analysis venous|venous blood gas test results : exporter exporters exporting Analysis of arterial and mixed venous blood provides information concerning the oxygenation, ventilatory, and acid-base status of the patient from whom the specimen was obtained. 1,878 likes, 102 comments - sandraalvesoficial on January 22, 2023: "Agenda da semana! #secristocomigovaieuirei "
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Para conhecer os conteúdos oficias do Fatal Model, clique aqui. Fechar. Acompanhantes trans e travestis em Teresópolis - RJ Mulheres Homens Trans Lary Bauer Offline há 24 minutos Últimos dias ! Cem A gosada! R$ 100/h 30 anos Com local 1 review Pimenteiras, Teresópolis - RJ Novo vídeo .
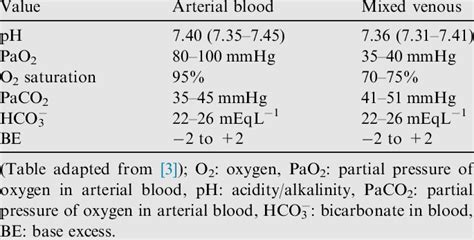
Venous blood gas (VBG) interpretation. Arterial blood gases (ABGs) are commonly used for estimating the acid-base status, oxygenation and carbon dioxide concentration of unwell patients. However, arterial blood can . The venous blood gas panel is one of the most useful tools we have to help us understand why the pH is deranged, and gives us information we don’t get from other laboratory panels. Specifically we can get a huge amount .
venous blood gas vs arterial
A blood gas sample can also be venous, from a vein or preexisting IV or capillary, which requires a small prick to the heel. Assessment of oxygenation: Advantages of pulse oximetry over ABG. Situations where ABG is needed to assess oxygenation: Poor arterial waveform. Dyshemoglobinemia. P/F ratio. A-a gradient. Patients with dark . Analysis of arterial and mixed venous blood provides information concerning the oxygenation, ventilatory, and acid-base status of the patient from whom the specimen was obtained.Venous blood gases (VBG) are widely used in the emergency setting in preference to arterial blood gases (ABG) as a result of research published since 2001. The weight of data suggests that venous pH has sufficient agreement .
The venous blood gas (VBG) is a multi-component serum assessment of pH, blood gas tensions (P v O 2 and P v CO 2), bicarbonate (HCO 3), and the base excess.
Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis is the gold standard method for assessment of oxygenation and acid base analysis, yielding valuable information about a variety of disease process. We searched MEDLINE, CINAHL, and Cochrane Library database for articles published between January 1990 and December 2012. The update of this clinical practice guideline is based on 237 clinical trials, 54 reviews, and . The only diagnosis which could be identified based on blood gas analysis was anxiety-related hyperventilation (HV). ABG/VBG to evaluate for hypercapnia. ABG/VBG is a useful tool to evaluate for hypercapnia. For .There’s also a test known as a "blood gas analysis," which uses a sample of blood from anywhere in your circulatory system (artery, vein or capillary). An arterial blood gas (ABG) test only tests a blood sample from an artery in your .
I NTRODUCTION. Arterial blood gas analysis is an important routine investigation to monitor the acid-base balance of patients, effectiveness of gas exchange, and the state of their voluntary respiratory control.[]In context of oral and maxillofacial surgery, arterial blood gas analysis plays a vital role in monitoring of postoperative patients, patients receiving oxygen therapy, those on .Laboratory orders and clinical documentation should clearly identify the origin of a venous sample for blood gas analysis. For example, there should be clear documentation to differentiate whether a venous sample was drawn from a peripheral stab or an indwelling central venous catheter. Central line samples should also identify the site of .
The Venous Blood Gas Panel 101 Posted on October 17, 2022 October 19, 2022 by Teaching Resident. By Lara Silverman MD/MPH, Emergency Medicine PGY3 October 2, 2022. Intro: Turns out most things in medicine are about acid-base disorders. A vent, understanding sepsis, kidney failure, respiratory failure, toxicology: so much of diagnosis and . Arterial blood gas (ABG) interpretation is something that can be difficult to grasp initially (we’ve been there). We’ve created this guide, which aims to provide a structured approach to ABG interpretation whilst also increasing your understanding of each result’s relevance. . Before getting stuck into the details of the analysis, it .Review article: Can venous blood gas analysis replace arterial in emergency medical care? Emerg Med Australas. 2010 Dec;22(6):493-8. PMID: 21143397. Kelly AM, McAlpine R, Kyle E. Venous pH can safely replace arterial pH in the initial evaluation of patients in the emergency department. Emerg Med J. 2001 Sep;18(5):340-2.
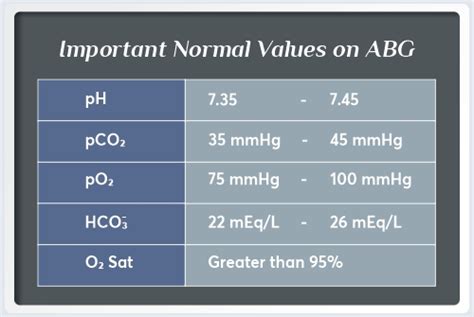
Arterial blood gas analysis; ABG; Hypoxia - ABG; Respiratory failure - ABG. Blood gases are a measurement of how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in your blood. They also determine the acidity (pH) of your blood. The blood gases test is performed by collecting a sample of blood through a needle from an artery. The test is used to evaluate . A blood gas test is also called an arterial blood gas test or a blood gas analysis. Results show blood oxygen and carbon dioxide levels, pH levels, and lung function. Doctors often use the test in .An arterial blood gas (ABG) test, or arterial blood gas analysis (ABGA) measures the amounts of arterial gases, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide.An ABG test requires that a small volume of blood be drawn from the radial artery with a syringe and a thin needle, [1] but sometimes the femoral artery in the groin or another site is used. The blood can also be drawn from an .Introduction Identifying acute hypercapnic respiratory failure is crucial in the initial management of acute exacerbations of COPD. Guidelines recommend obtaining arterial blood samples but these are more difficult to obtain than venous. We assessed whether blood gas values derived from venous blood could replace arterial at initial assessment. Methods Patients requiring hospital .
Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gases (ABGs) David A. Kaufman, MD Chief, Section of Pulmonary, Critical Care & Sleep Medicine Bridgeport Hospital-Yale New Haven Health Assistant Clinical Professor, Yale University School of Medicine (Section of Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine) Introduction: Interpreting an arterial blood gas (ABG) is a crucial skill for physicians, . A venous blood sample is drawn for ScvO2 measurement. Continuous vs. Intermittent Measurement of Venous Saturation. ScvO2 or SmvO2 can be measured by drawing blood from the distal line of CVC or PAC for blood gas analysis. It can also be measured continuously using a fibreoptic catheter that uses reflection spectrophotometry.An arterial blood gas (ABG) test measures oxygen, carbon dioxide, and acidity in a blood sample to see how well your lungs, heart and kidneys are working. Learn more. Unlike arterial blood gas analysis, which requires a sample of blood taken from an artery, venous blood gas analysis uses a sample of blood taken from a vein. The most common site for venous blood collection is the median cubital vein in the antecubital fossa, although other peripheral veins can also be used.
Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis is a frequently ordered test in intensive care unit (ICU) and can analyze electrolyte in addition to pH and blood gases. Venous blood gas (VBG) analysis is a safer procedure and may be an alternative for ABG. Electrolyte estimation by auto analyzer usually takes 20–30 minutes.
Blood gas analysis is probably the most common diagnostic tool used in intensive care. In fact, a proper understanding and use of arterial and pulmonary/central venous blood gas and electrolytes analysis makes it possible to correctly interpret most of the respiratory, circulatory and metabolic derangements which may occur in critically ill patients. Background Blood gas analysis is integral to assessing emergency department (ED) patients with acute respiratory or metabolic disease. Arterial blood gas (ABG) is the gold standard for oxygenation, ventilation, and acid–base status but is painful to obtain. Peripheral venous blood gas (VBG) is a valuable alternative as it is less painful and easy to collect. The .
Peripheral venous blood gas (PVBG) analysis was first described as an alternative to ABG sampling by Dautrebande, Davis and Meakins in 1923 when they measured the CO 2 content of venous blood obtained from the basilic vein in four experiments and found a close correlation with that of arterial blood if the hand was immersed in hot water . Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis is used in critical care units to determine the degree of oxygenation, adequacy of ventilation, and the presence and severity of acid-base disturbances in the body. However, arterial puncture may result in complications, and the difficulty in acquiring arterial blood may delay care. .
venous blood gas test results
A blood gas test or blood gas analysis tests blood to measure blood gas tension values, it also measures blood pH, and the level and base excess of bicarbonate.The source of the blood is reflected in the name of each test; arterial blood gases come from arteries, venous blood gases come from veins and capillary blood gases come from capillaries. [1] The blood gas .Aims: Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis is a frequently ordered test in intensive care unit (ICU) and can analyze electrolyte in addition to pH and blood gases. Venous blood gas (VBG) analysis is a safer procedure and may be an alternative for ABG. Electrolyte estimation by auto analyzer usually takes 20-30 minutes.We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
Blood gas analysis is integral to assessing emergency department (ED) patients with acute respiratory or metabolic disease. Arterial blood gas (ABG) is the gold standard for oxygenation, ventilation, and acid–base status but is painful to obtain. Peripheral venous blood gas (VBG) is a valuable alternative as it is less painful and easy to . James et al. reported in 1958 that gas analysis of blood samples obtained from a clamped umbilical cord could reflect fetal hypoxia.[1] Since then, cord blood gas analysis has become widely performed to objectively determine the fetal metabolic condition at the time of delivery when umbilical circulation stops.[2] Multiple studies showed that this analysis, when .
Blood-gas-analysis-derived over-distension results from both "true" and "functional" over-distension . We found that Qs/Qt + Vd/Vt derived PEEP was occasionally higher than EIT-derived PEEP, contrary to expectations. While individual animals showed variable optimal PEEP values across methods, averaged data indicated a consistent range of 16 .
Gas Permeability Test System mfg
venous blood gas sample
Resultado da Are you interested in becoming a Professional Home Economist (P.H.Ec)? To become a P.H.Ec. in Ontario, you need a degree from a university .
gas analysis venous|venous blood gas test results